Overview of oscillators
Definition Oscillator
An oscillator is an oscillatory system that is used to generate a stable and accurate time base. These systems typically utilize crystal oscillators, such as the Temperature Controlled Crystal Oscillator (TCXO) or the even more precise Oven Controlled Crystal Oscillator (OCXO). These oscillators are important for maintaining accurate time synchronization in networks by providing a continuous and stable time reference even when there is no connection to an external time source (such as GPS or an NTP Server). The choice of oscillator type depends on the required accuracy and stability requirements
The different, most common oscillators
Uncompensated quartz oscillators that can be realized in various basic circuits such as Pierce, Colpitts or Clapp. Their frequency stability is less precise compared to other types.
Our XO oscillators:
It's the base for synchronization
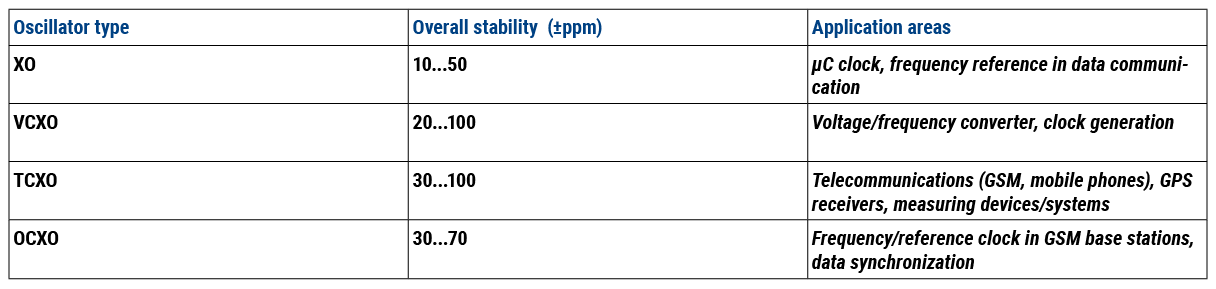
Oscillators are responsible for generating oscillations or clock signals, which form the basis for synchronization and timing in a variety of applications. Depending on the required precision and stability of the signal, different types of oscillators are used. The selection of an oscillator depends largely on its overall stability and the specific requirements of the application. A distinction is mainly made between simple crystal oscillators (XO), voltage-controlled crystal oscillators (VCXO), temperature-compensated crystal oscillators (TCXO) and oven-controlled crystal oscillators (OCXO), each of which is used in specific application areas such as data communication, telecommunications and precision measurement systems. The overview below provides an insight into the typical characteristics and application areas of different oscillator types to enable an informed selection for specific technical requirements.