What is an DDoS attack?
A distributed denial-of-service (DDoS) attack is a particular form of cyber-crime that is considered a variant of a denial-of-service (DoS) attack. In a DDoS attack, a requested service is either completely blocked or its availability is significantly restricted. This is typically done by deliberately overloading the target's IT infrastructure. Such attacks are often used by cyber criminals to blackmail unprotected organizations by demanding a ransom or to carry out, conceal or prepare other criminal activities.
What is a NTP amplification attack and how does it work?
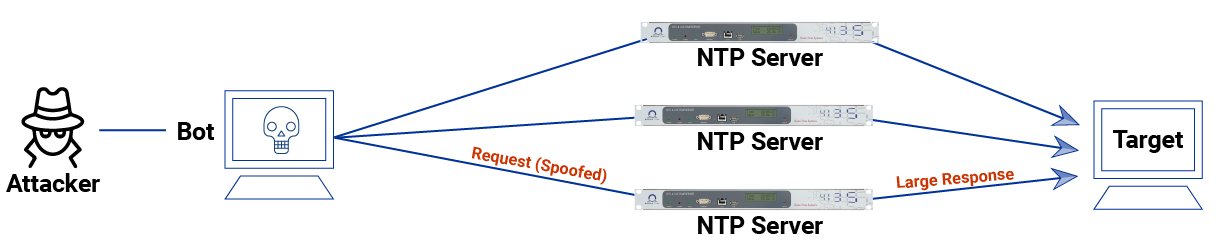
NTP is a UDP-based protocol that is used to synchronise computer clocks on the Internet. Attackers exploit it to amplify DDoS attacks:
- The attacker spoofs the victim's IP address and sends a small UDP request to a vulnerable NTP server.
- The NTP server thinks the request is legitimate and sends a much larger UDP response back to the spoofed victim's IP address.
- By forwarding responses from thousands of NTP servers, the attacker uses amplification factors of 50x, 100x or more.
- This allows relatively small requests of just a few kilobits to generate gigabits or terabits of attack traffic that floods the victim.
- Common NTP commands such as monlist are abused to generate large responses.
Amplification effects in NTP: The 'monlist' command and its effects
Amplification results from the use of certain NTP commands that convert a small request into a large response. A frequently used example is the "monlist" command, which returns a list of the last 600 hosts that have contacted the NTP server. This response can be very large and therefore cause a considerable amplification.
Strengthen NTP server security

Learn here how you can strengthen the security of your NTP time servers. You can expect effective methods to fend off DDoS attacks and protect your network.